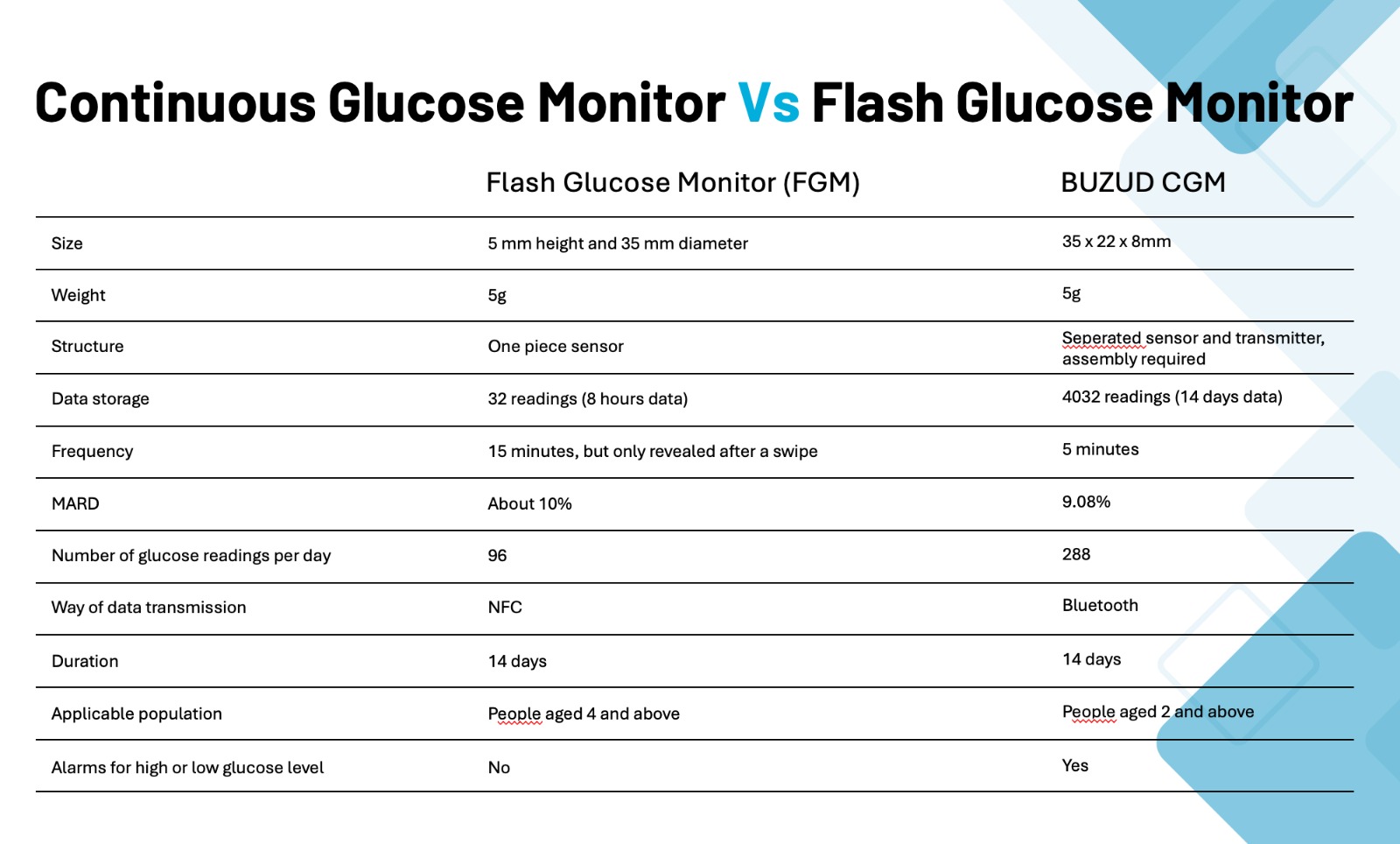
Understanding FGM vs. CGM: What’s the Difference?
When managing diabetes, knowing your glucose levels is crucial. Two popular technologies help with this: Flash Glucose Monitoring (FGM) and BUZUD Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM). While they might seem similar, they have distinct differences that could impact your daily life. Let’s break them down in an easy-to-understand way.
Manual Scanning vs. Real-Time Readings
FGM (Flash Glucose Monitoring):
- How it works: You wear a small sensor on your skin, usually on the back of your arm.
- Data access: To see your glucose levels, you need to manually scan the sensor with a reader or smartphone app. This means you only get the glucose data when you scan it.
BUZUD CGM (Continuous Glucose Monitoring):
- How it works: Similar to FGM, you wear a sensor on your skin, but it continuously measures your glucose levels.
- Data access: Glucose readings are automatically sent to your device (a receiver, smartphone, or smartwatch) in real time, typically every 5 minutes.
Alerts and Notifications
FGM:
- Alerts: Typically, FGM systems do not offer real-time alerts for high or low glucose levels. You have to scan to get your glucose reading and see trends.
- Who it’s for: Ideal for those who prefer fewer alarms and don’t need constant monitoring.
BUZUD CGM:
- Alerts: One of the biggest advantages of CGM is the ability to set customizable alerts. These alerts notify you if your glucose levels go too high or too low, helping prevent dangerous situations.
- Who it’s for: Perfect for those needing continuous monitoring and proactive alerts, like children, pregnant women, or people with frequent hypo or hyperglycemic episodes.
Data Storage and Insights
FGM:
- Data storage: When you scan your sensor, the data is stored in the device. You can download it later to review trends and patterns.
- Insights: Useful for understanding how your glucose levels change over time but requires you to be proactive in scanning and analyzing the data.
BUZUD CGM:
- Data storage: CGMs continuously record glucose levels, storing this data in the cloud or on your device. You can access comprehensive reports and trends anytime.
- Insights: Provides detailed insights and trends, often with more sophisticated data analysis tools. This continuous data can be shared with your healthcare provider in real time for better management.
Number of Glucose Readings Per Day
FGM:
- Readings per day: 96 readings (measured every 15 minutes).
- Implications: With FGM, the sensor records glucose levels every 15 minutes, resulting in 96 readings per day. However, you only access this data when you scan the sensor, which means the data is not constantly available to you in real time. This system provides a detailed snapshot of your glucose levels over time but requires user interaction to access the information.
BUZUD CGM:
- Readings per day: 288 readings (measured every 5 minutes).
- Implications: CGM systems provide a much higher resolution of glucose monitoring by measuring glucose levels every 5 minutes, resulting in 288 readings per day. This continuous stream of data is automatically sent to your device, allowing for real-time monitoring and immediate alerts. This high frequency of readings offers a more comprehensive picture of glucose trends and variations throughout the day.

Photo by Patty Brito on Unsplash
Applicable Population
FGM:
- Age range: Suitable for people aged 4 and above.
- Implications: FGM systems are generally approved for use in individuals aged 4 and older. This makes FGM a versatile option for a broad range of users, from young children to older adults, offering flexibility for family use.
BUZUD CGM:
- Age range: Suitable for people aged 2 and above.
- Implications: BUZUD CGM systems are approved for even younger children, starting at age 2. This broader age range can be particularly beneficial for very young children who require closer glucose monitoring due to more unpredictable glucose swings or who may be unable to articulate symptoms of hypo- or hyperglycemia effectively.
Mean Absolute Relative Difference (MARD)
FGM:
- MARD value: Typically ranges between 9% to 14%.
- Implications: MARD is a measure of accuracy for glucose monitoring systems, indicating the average absolute difference between the glucose values reported by the monitoring system and the reference glucose values. An FGM system with a MARD of 9% to 14% means that on average, the glucose readings are within this percentage range of the true glucose value. While this is fairly accurate, there may be occasional deviations that require confirmation with a finger prick test.
BUZUD CGM:
- MARD value: Typically ranges between 8% to 12%.
- Implications: CGM systems tend to have a slightly lower MARD value, indicating higher accuracy compared to FGM systems. A MARD of 8% to 12% means that the CGM readings are more consistently close to the true glucose values. This higher accuracy can be particularly beneficial for making real-time decisions about insulin dosing, diet, and activity levels, thereby improving overall diabetes management.
Way of Transmission
FGM:
- Transmission method: Uses Near Field Communication (NFC) to transfer data when you scan the sensor with a reader or smartphone.
- Implications: NFC technology requires close proximity scanning to transfer data. This method is simple and effective but means you need to remember to scan the sensor periodically to get your glucose readings. It’s a bit like tapping your contactless credit card – it’s quick and easy but requires you to initiate the action.
BUZUD CGM:
- Transmission method: Uses Bluetooth to continuously transmit data in real time to your device.
- Implications: Bluetooth technology allows for a constant stream of data to be sent from the sensor to your device without manual intervention. This real-time transmission is seamless and automatic, providing continuous glucose updates and ensuring you are always informed of your current glucose status, which is particularly useful for managing sugar levels or diabetes more proactively.
While both FGM and CGM have their benefits and drawbacks, CGM stands out for its comprehensive and proactive approach to glucose monitoring. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision about which technology best fits your lifestyle and health needs. The automated, real-time data from CGM, coupled with continuous alerts and detailed insights, provides a significant advantage in managing diabetes effectively. Choosing CGM can lead to better glucose control and peace of mind, knowing you are constantly informed of your glucose levels without the need for manual scans.
If you need assistance, you can visit our BUZUD showroom for calibration support.
DISCLAIMER
All information presented herein serves as a general guideline, and is not intended as dispensing any medical advice(s). User(s) should consult their doctor to seek further clarification for any doubt. It is recommended to refer to this guide with sole discretion, thereby we shall not be held responsible for any part of the information as presented.
REimagined Healthcare with BUZUD Care Experience at:
585 North Bridge Road, #01-02 Raffles Hospital, Singapore 188770
Call: +65 6518 9959 or Email: customercare@BUZUD.com
No Comments
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
